What we do
About our project
Background
Atherosclerosis is a lipid- and inflammation-driven disease of the arteries that is characterized by fatty-streak development and subsequent plaque formation. Plaque rupture is the main cause of acute coronary syndromes. Traditionally, the burden of atherosclerotic disease is estimated from the percentage of stenosis detected by coronary angiography. Coronary angiography is a valuable tool to assess coronary heart disease, but is invasive in nature and cannot detect rupture-prone atherosclerotic plaques. An additional imaging tool aimed at characterizing atherosclerosis of the coronary tree is required to identify patients at risk, and would allow targeted treatment.
Aim
We aim at detecting inflammation and calcification as targets for radionuclide imaging to assess atherosclerotic plaque composition as plaque composition is linked to rupture risk. The ultimate goal is to develop new diagnostic imaging and discover new treatment targets for atherosclerosis.
Approach
We make use of (pre-)clinical models and patient samples. Our studies include multiple radioligands targeting inflammatory cell subsets and (micro)calcifications in atherosclerotic plaques. Radioligand uptake specificity is validated by immunohistochemical analysis of the targets.
- Characterize the presence of the target in human atherosclerosis samples.
- Test the radioligand for the in vivo detection of its target in pre-clinical models of atherosclerosis
- Detect atherosclerosis in patients by non-invasive radioligand imaging
Our research focus
Funds & Grants
Erasmus MC grant, a grant to stimulate collaborations between clinical and pre‐clinical researchers for project ”Non‐invasive molecular imaging of inflammation to detect atherosclerosis” (2014-2020)
European Union Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions grant number: 707404
Collaborations
Collaborations within Erasmus MC:
-Cardiology department
-Radiology and Nuclear medicine Department
-Applied Molecular Imaging Core Facility
Publications
Imaging inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques, targeting SST 2 with [ 111 In]In-DOTA-JR11
Perspectives on Radionuclide Imaging; Considerations and Advances in Atherosclerosis.
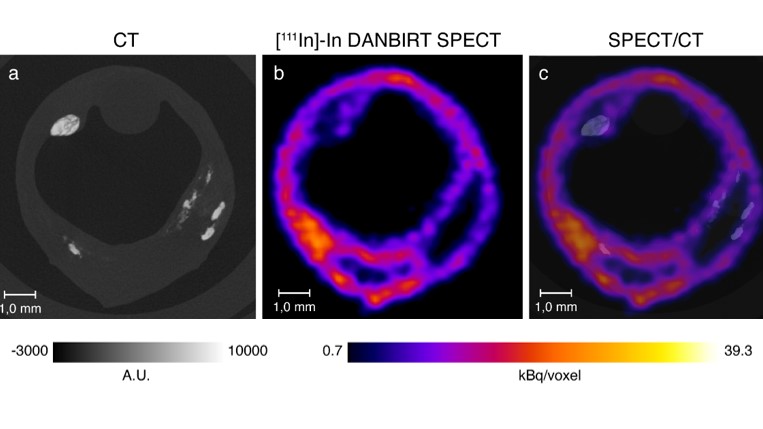
Imaging of atherosclerosis, targeting LFA-1 on inflammatory cells with 111InDANBIRT.
Our team
- Dr. M.R. (Monique) Bernsen, PhD, Head daily management
- Dr. B.J. (Boudewijn) Krenning, MD, PhD, Cardiologist Erasmus MC en Franciscus Gasthuis & Vlietland


